Tree species composition is known to affect forest productivity, but also affects forest adaptation Disturbances such as storm impacts remain largely unexplored.
In Europe, tree mortality caused by storms is increasing in all climate biomes. Understand the factors that determine forest resilience to storms and their consistency across climates It is therefore crucial for predicting the consequences of climate change on forests around the world.
A group of researchers from the French National Institute for Research in Agriculture, Food and the Environment (INRAE) Typical scenarios where vegetation diversity is a key factorThe results obtained were quite convincing regarding the resilience of forests to the impact of climate change.
According to a recent study published in the journal Functional environmentEuropean forests with the greatest diversity of tree species They tend to be more resistant to storms where heavy rains and winds are common.
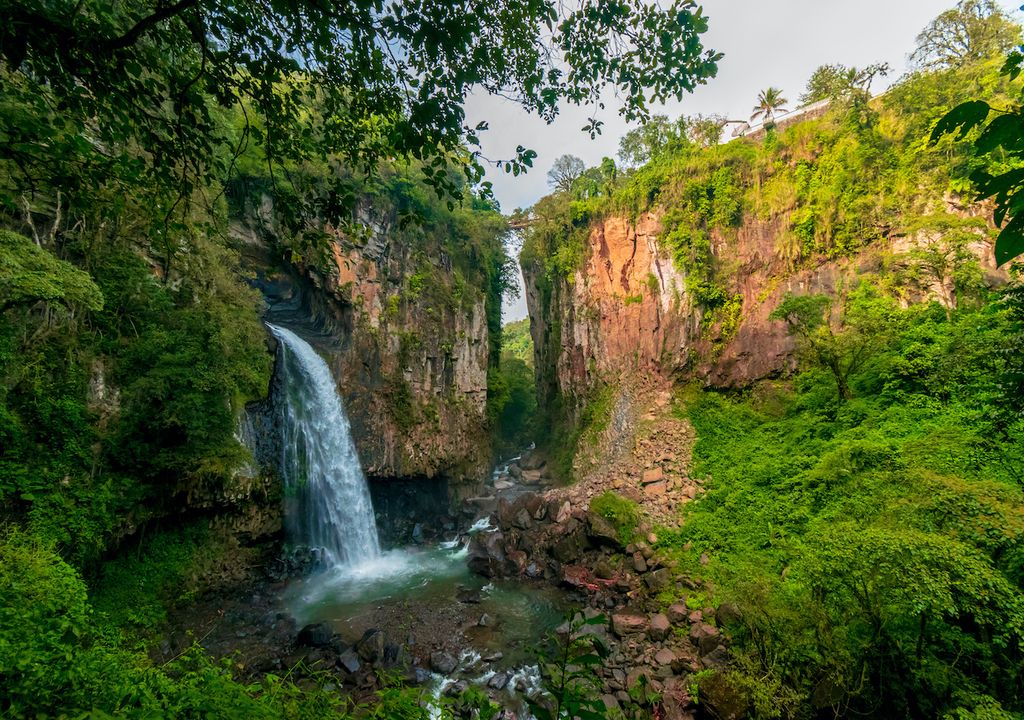

The researchers found that in areas with diverse vegetation areas enriched with different types of plants, Particularly diverse trees, dominated by slow-growing, high-density species, showed greater resistance to weather storms.
They also found that the positive effect of tree diversity on storm resilience was more pronounced in extreme weather conditions. Such as hot and dry conditions in the Mediterranean region and cold and humid conditions in northern Scandinavia.
Methodology: Tree cover modeling systems
The study used simulations to model how forests with different characteristics, such as tree species diversity, resist and recover from storm damage.
In recent decades, Europe has experienced more frequent and intense wind storms, putting forests and the ecosystem services they provide at risksuch as habitats, carbon storage and wood.
Hey Dr. Julien Barriere“An important conclusion from our study is that monocultures of fast-growing species such as pine, despite their economic value, are more vulnerable to storm damage,” said the INRAE researcher and lead author of the study. “In the context of increasing losses due to supercells in all Across the continent, our study advocates for forest management practices that promote diversity and slow-growing tree species such as oak.
In the study, the researchers created a model to simulate the dynamics of hundreds of forests after a storm. Model calibration with data from 91,528 real forest plots in Europe.
“Our simulated forests varied in terms of climatic conditions, from the Mediterranean to the north, and in composition, that is, the diversity and identity of tree species,” explained Dr. Barrier. “This allowed us to measure The relationship between forest composition and storm resilience How does this relationship change along the European climate gradient?
The researchers caution that this is a pilot study. Field work is still necessary to confirm this discovery. “While modeling studies like ours are necessary to draw conclusions about forest dynamics due to the long time scales in nature, results must be interpreted with a clear understanding of model assumptions and complemented by field studies,” said Dr. Barrier.
Evolution in adaptation to forests
Show results Climate composition and tree species interact to control the ability of forests to withstand and recover from a storm Through direct and indirect influences. As such, our results should be Helping better predict the consequences of climate change on forest ecosystems.
This fact confirms the well-known theory Barrier effect What trees do to confront severe storms that can occur during hurricane season in tropical regions. However, researchers say, this is a topic that needs more in-depth study.

“Hardcore beer fanatic. Falls down a lot. Professional coffee fan. Music ninja.”




More Stories
Science may have found the origin of altered states of consciousness
A highly contagious virus fills hospitals in Brazil
Do we all feel that time passes in the same way?